The Bioinformatics Resource Facility (BRF) as part of the Technology Platform Bioinformatics at the Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec) has a strong focus on the development of innovative bioinformatics software tools. The design and implementation of novel features is driven by our close collaboration with researchers of the center. Within many projects, experimental data are produced by the CeBiTec Technology Platform Genomics and it is therefore one of our major goals to simplify and automate the subsequent steps for a systematic data processing and analysis as far as possible. For the development of larger software platforms we follow the design principle to build specialized tools for separate scopes that can be interlinked to integrate the various data resources. Technically, we can rely on an extensive hardware infrastructure that provides all necessary storage and compute capacities.
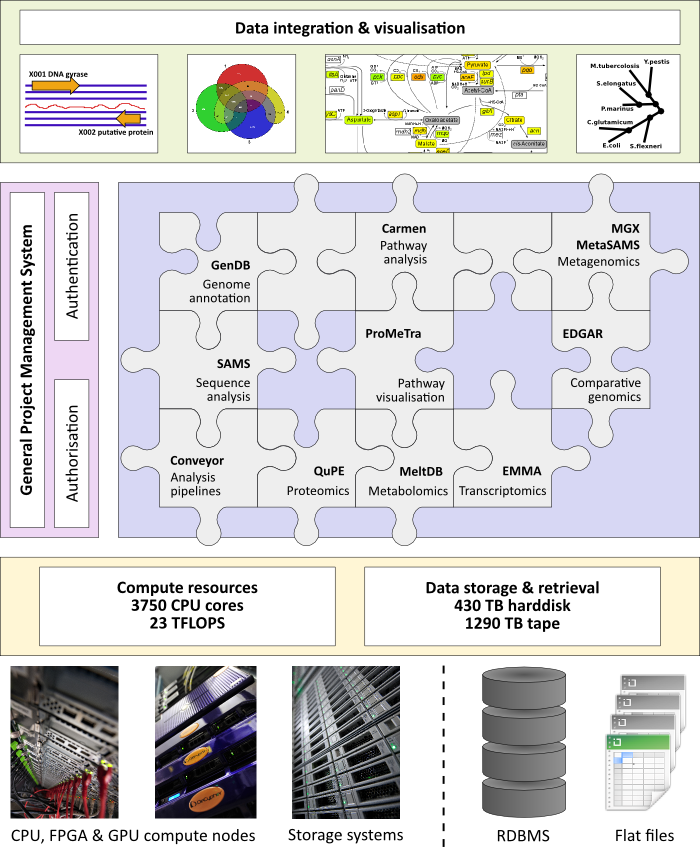
Applications developed in the field of genomics comprise the maintenance and annotation of complete genomes as well as the evaluation of other sequence data employing the GenDB and SAMS software. While the GenDB system was successfully used for the automatic and manual annotation of more than 150 microbial genomes, SAMS is routinely applied for detailed analyses of large sequence sets (ESTs or metagenome reads). Based on the genome annotation data provided by GenDB, the CARMEN application can perform a metabolic reconstruction. CARMEN provides two main applications: the generation of de novo models based on KEGG database information and the creation of template based SBML models for comparative genomics. An organism-specific network model of individual or large-scale metabolic pathways can be reconstructed based on genome annotation data that can be obtained from GenDB or alternatively loaded from NCBI GenBank files.
In the field of transcriptomics, the EMMA software is provided as a MAGE-compliant software platform for the evaluation of data resulting from genome-wide transcriptomic studies. Detailed experimental setups and protocols as well as all raw data sets are stored in a separate LIMS component (ArrayLIMS). QuPE is an application for large-scale analyses of proteome data, also including a LIMS component. Furthermore, the MeltDB software was developed for the high-throughput analysis of experimental data from metabolome analyses. All components are linked via the BRIDGE integration layer providing an interface for further data mining, modeling, simulation, and visualization approaches. The ProMeTra application is one example for the ongoing development of novel software tools to support researchers in the field of systems biology. ProMeTra uses web services technology to enrich metabolic pathway maps with quantitative results stored within EMMA, QuPE, and MeltDB.



